publications
You can also check my Google Scholar profile.
2024
- INFFUS
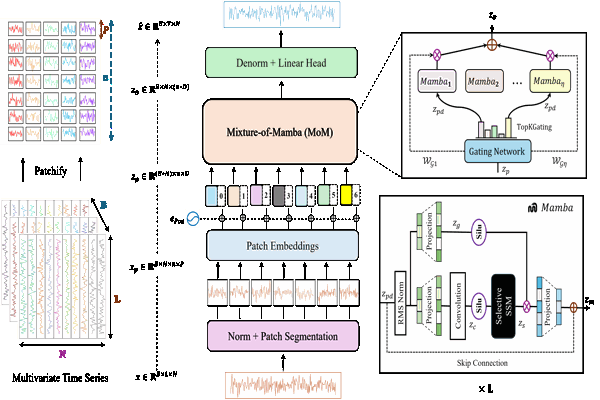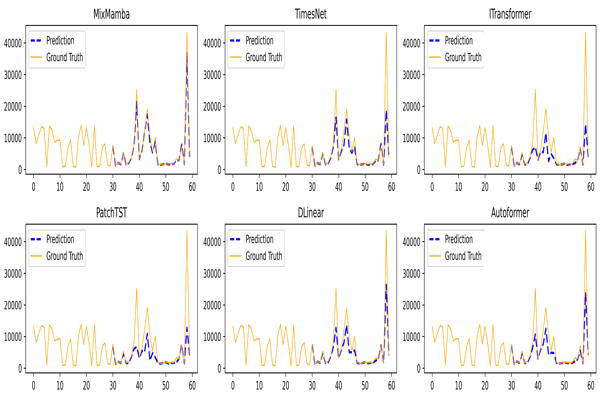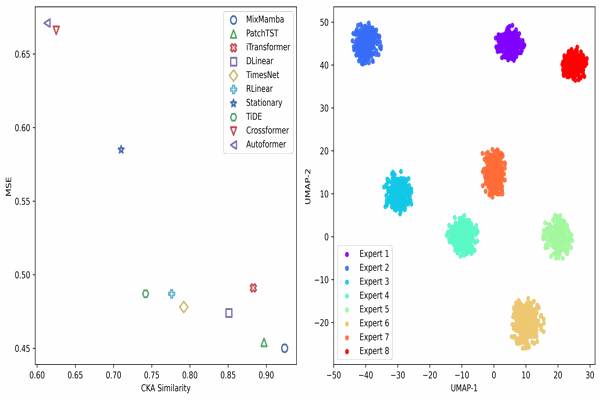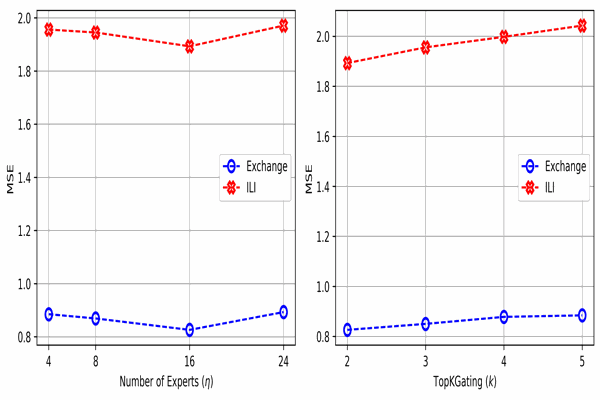 MixMamba: Time series modeling with adaptive expertiseKhaled Alkilane, Yihang He, and Der-Horng LeeInformation Fusion, 2024
MixMamba: Time series modeling with adaptive expertiseKhaled Alkilane, Yihang He, and Der-Horng LeeInformation Fusion, 2024From finance and healthcare to transportation and beyond, effective time series modeling underpins a wide range of applications. While transformers have achieved success, their reliance on global context limits scalability for lengthy sequences due to the quadratic increase in computational cost with sequence length. Recent research suggests linear models can achieve comparable performance with lower complexity. However, the heterogeneity and non-stationary characteristics of time series data continue to challenge single models’ ability to capture complex temporal dynamics, especially in long-term forecasting. This paper proposes MixMamba, a novel framework for time series modeling applicable across diverse domains. The framework leverages the content-based reasoning strengths of the Mamba model by integrating it as an expert within a mixture-of-experts (MoE) framework. This framework decomposes modeling into a pool of specialized experts, enabling the model to learn robust representations and capture the full spectrum of patterns present in time series data. Furthermore, a dynamic gating network is introduced within the framework. This network adaptively allocates each data segment to the most suitable expert based on its characteristics. This is crucial in non-stationary time series, as it allows the model to adjust dynamically to temporal changes in the underlying data distribution. To prevent bias towards a limited subset of experts, a load balancing loss function is incorporated. Extensive experiments on benchmark datasets demonstrate the effectiveness and robustness of our proposed method in various time series modeling tasks, including long-term and short-term forecasting, as well as classification.
@article{ALKILANE2024102589, title = {MixMamba: Time series modeling with adaptive expertise}, journal = {Information Fusion}, volume = {112}, pages = {102589}, year = {2024}, issn = {1566-2535}, doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2024.102589}, url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1566253524003671}, author = {Alkilane, Khaled and He, Yihang and Lee, Der-Horng}, keywords = {Time series modeling, Mixture-of-experts, Multivariate time series forecasting}, } - KBS
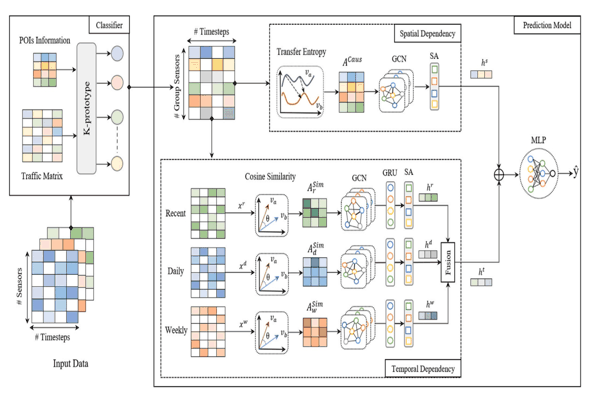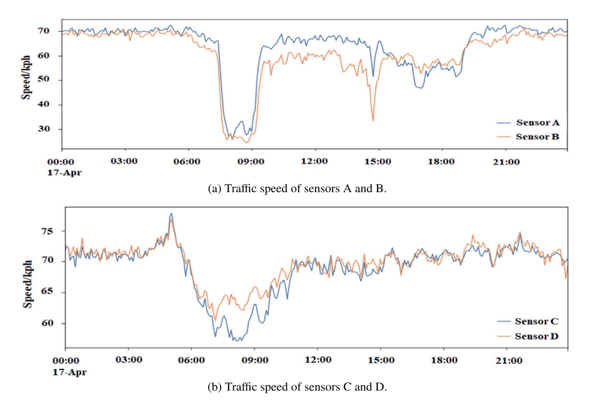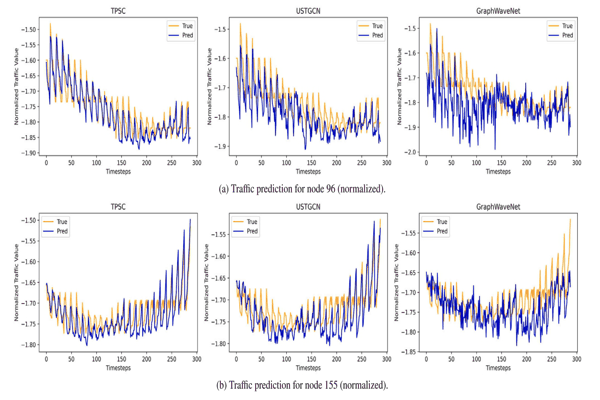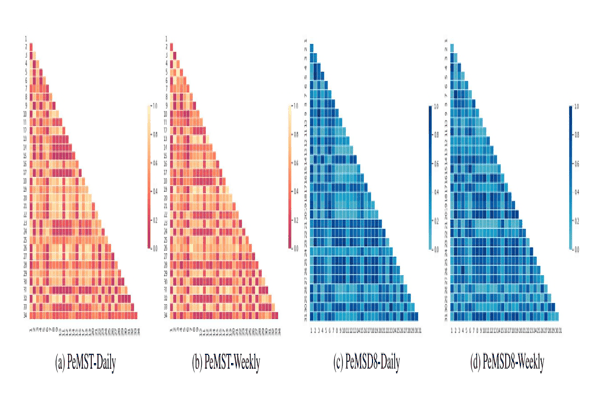 A graph-based approach for traffic prediction using similarity and causal relations between nodesKhaled Alkilane, Alfateh M. Tag Elsir, Pengfei Wang, and 2 more authorsKnowledge-Based Systems, 2024
A graph-based approach for traffic prediction using similarity and causal relations between nodesKhaled Alkilane, Alfateh M. Tag Elsir, Pengfei Wang, and 2 more authorsKnowledge-Based Systems, 2024Accurate traffic prediction is crucial for the development of intelligent transportation systems (ITS) and various smart applications. To achieve this, effectively capturing the complex interplay between spatial and temporal dependencies across traffic nodes is essential. However, existing research often focuses solely on fixed spatial dependencies between neighboring nodes, neglecting the potential influence of distant nodes. This paper addresses these limitations by exploring two key types of relationships among traffic nodes. First, we examine indirect relationships based on similarity, where nodes exhibit similar traffic patterns irrespective of their physical proximity. Second, we investigate direct causal relationships, where traffic conditions at one node are directly influenced by other nodes. Based on these findings, we propose a novel approach named TPSC (Traffic Prediction using nodes Similarity and Causal relations). TPSC incorporates a classifier that utilizes the K-Prototype algorithm to group nodes based on their traffic similarity and nearby points of interest (POIs). Separate models are then trained for each cluster. Our model leverages a spatial module that employs graph convolutional network representation learning alongside transfer entropy to capture causal relationships and dynamic spatial dependencies. Additionally, a temporal module is introduced to capture periodic temporal dependencies across three components: recent patterns, daily patterns, and weekly patterns. Extensive experiments are conducted to evaluate proposed model on four large-scale traffic datasets for multiple traffic characteristics including speed, flow, and travel time. The experimental results demonstrate that TPSC surpasses the performance of the compared baselines, highlighting its superior predictive capabilities in traffic prediction.
@article{KHALED2024111913, title = {A graph-based approach for traffic prediction using similarity and causal relations between nodes}, journal = {Knowledge-Based Systems}, volume = {296}, pages = {111913}, year = {2024}, issn = {0950-7051}, doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2024.111913}, url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0950705124005471}, author = {Alkilane, Khaled and Elsir, Alfateh M. Tag and Wang, Pengfei and Shen, Yanming and Zhang, Qiang}, keywords = {Traffic prediction, Spatial–temporal correlations, Graph neural networks, Traffic similarity}, }
2023
- Expert Syst. Appl.
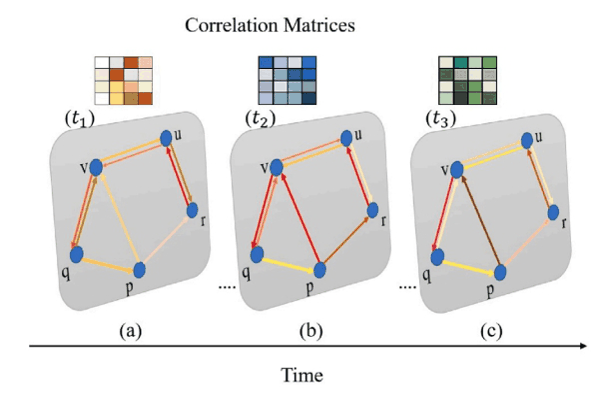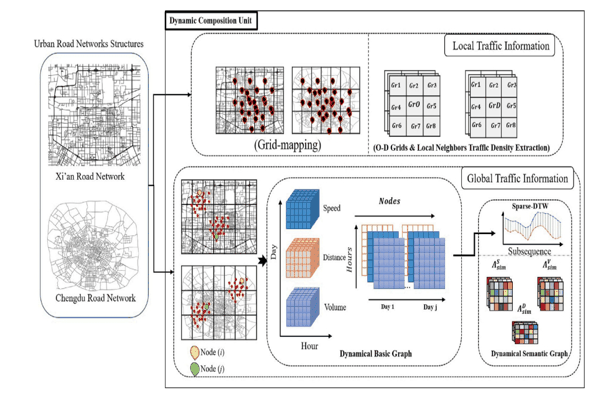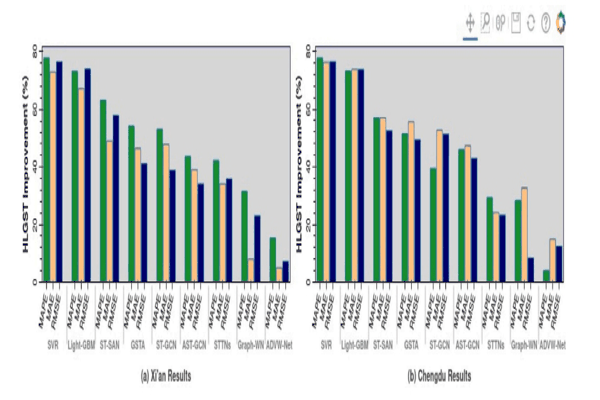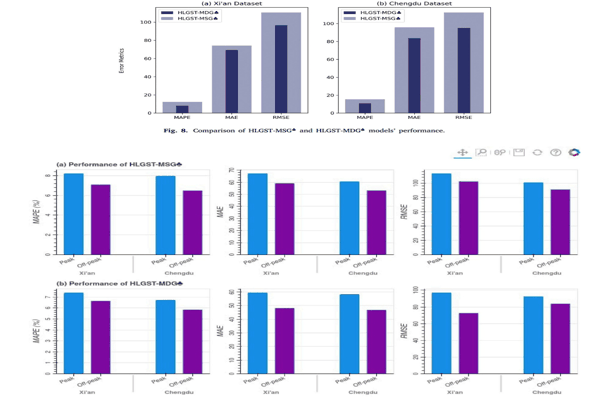 HLGST: Hybrid local–global spatio-temporal model for travel time estimation using Siamese graph convolutional with triplet networksAlfateh M. Tag Elsir, Khaled Alkilane, and Yanming ShenExpert Systems with Applications, 2023
HLGST: Hybrid local–global spatio-temporal model for travel time estimation using Siamese graph convolutional with triplet networksAlfateh M. Tag Elsir, Khaled Alkilane, and Yanming ShenExpert Systems with Applications, 2023Travel time estimation (TTE) is a crucial and challenging task due to the complex spatial and dynamic temporal correlations between local and global traffic regions. Though many existing methods have used multi-graph structures to model traffic variations, the majority of them are unable to capture such sophisticated local and global perspectives dynamically at different time-intervals. Furthermore, these methods have used shallow graphs (i.e., based on speed or distance between traffic nodes), thereby limiting their ability to learn the latent dependencies. To overcome these limitations, we propose a novel Hybrid Local-Global Spatio-Temporal (HLGST) framework for TTE. Specifically, we first introduce a dynamic composition unit that builds local traffic information and multi-dynamic semantic graphs based on the similarities between nodes. Then, the HLGST model learns the local and global dependencies via hybrid correlation method. It mainly comprises two modules: (1) local correlation module that integrates casual TCN layers with a self-attention mechanism to capture local dependencies of traffic patterns; (2) triplet-siamese GCN (TS-GCN) module that is employed to smoothly capture global dependencies based on triplet relationships between multi-dynamical semantic graphs. Moreover, we build a dynamic adaptive learning algorithm to transfer the gained knowledge and leverage it to model multi-objective prediction tasks collaboratively. Extensive experiments conducted on two real-world traffic datasets (Xi’an and Chengdu) demonstrate that our HLGST model outperforms compared baselines and achieves significant improvement.
@article{TAGELSIR2023120502, title = {HLGST: Hybrid local–global spatio-temporal model for travel time estimation using Siamese graph convolutional with triplet networks}, journal = {Expert Systems with Applications}, volume = {229}, pages = {120502}, year = {2023}, issn = {0957-4174}, doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2023.120502}, url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0957417423010047}, author = {{Tag Elsir}, Alfateh M. and Alkilane, Khaled and Shen, Yanming}, keywords = {Travel time estimation, Graph convolution network, Spatio-temporal correlations, Dynamic multi-graph, Semantic graph} } - IJCNN
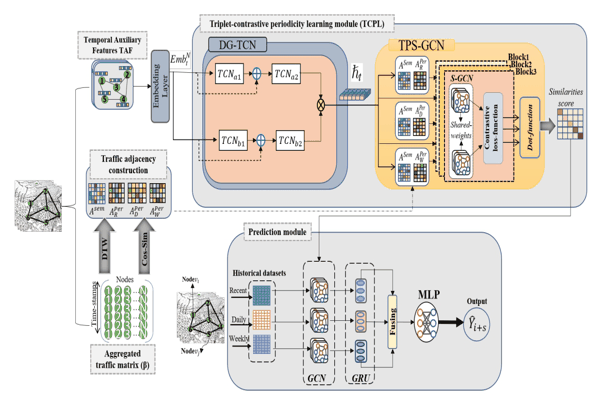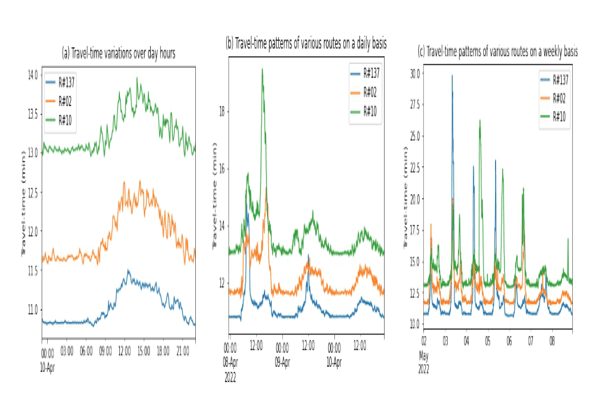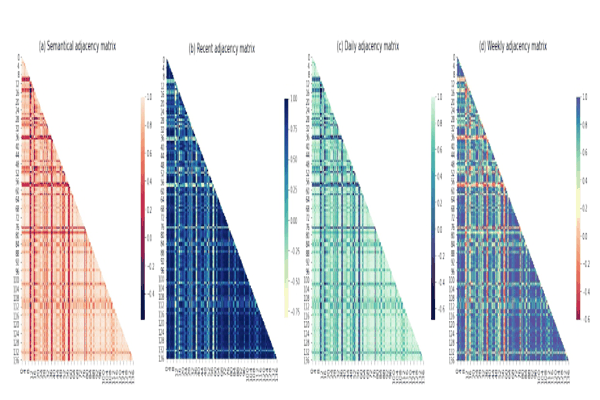 Triplet-contrastive Periodical Siamese Graph Networks for Travel Time EstimationElsir Alfateh M. Tag, Khaled Alkilane, and Shen YanmingIn 2023 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), 2023
Triplet-contrastive Periodical Siamese Graph Networks for Travel Time EstimationElsir Alfateh M. Tag, Khaled Alkilane, and Shen YanmingIn 2023 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), 2023Accurate travel time estimation (TTE) is a critical component of intelligent transportation systems (ITSs). However, due to the high variation and complexity of road networks, the majority of prior methods are inefficient to extracting both spatial and temporal dynamic correlations. Additionally, most of them often use simplistic graph representations to depict the traffic nodes’ interconnections and separate temporal modules to capture time variations. Thus, taking into account the semantic relationships among traffic variables is a difficult task that plays a crucial role in gaining a comprehensive understanding of traffic networks’ topology. To overcome these limitations, we propose a new deep learning framework called Triplet-Contrastive Periodical Siamese Graph networks (TCPSG). This framework incorporates a novel combination of Siamese graph networks and triplet contrastive learning, as well as considering periodicity patterns in traffic. Specifically, we construct semantical and periodical graph adjacency matrices that represent latent spatial correlations between nodes and periodicity dependencies of recent, daily, and weekly time-periods. Then, we devise a contrastivebased learning method that combines a triplet siamese graph structure with a dual-gated Temporal Convolutional Network (TCN) based module to simultaneously learn traffic patterns’ similarities among those three periodic components and longterm dynamic temporal dependencies. Extensive experiments on real-world traffic datasets demonstrate that TCPSG consistently outperforms baselines in all prediction horizons.
@inproceedings{10191875, author = {Tag, Elsir Alfateh M. and Alkilane, Khaled and Yanming, Shen}, booktitle = {2023 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN)}, title = {Triplet-contrastive Periodical Siamese Graph Networks for Travel Time Estimation}, year = {2023}, volume = {}, number = {}, pages = {1-8}, keywords = {Correlation;Roads;Semantics;Estimation;Traffic control;Predictive models;Feature extraction;Contrasitve Learning;Siamese Graph Networks;Spatial-Temporal Correlations;Travel-Time Estimation}, doi = {10.1109/IJCNN54540.2023.10191875}, } - Neural Comput. Appl.
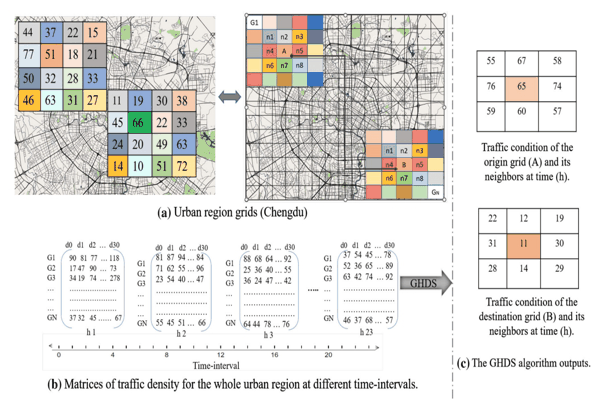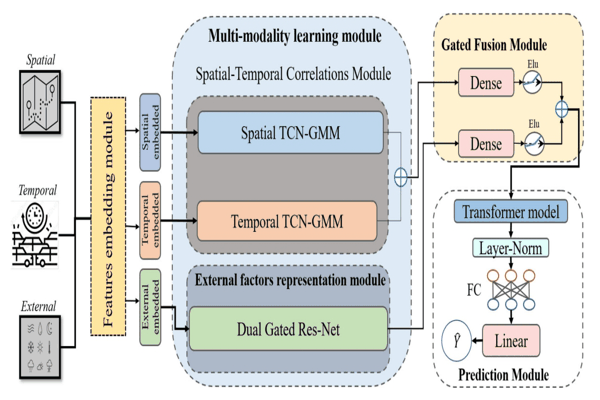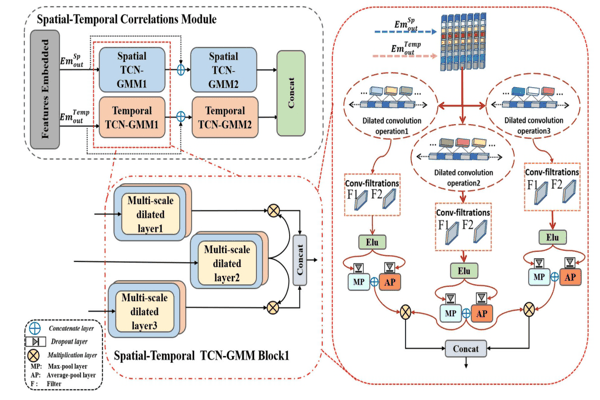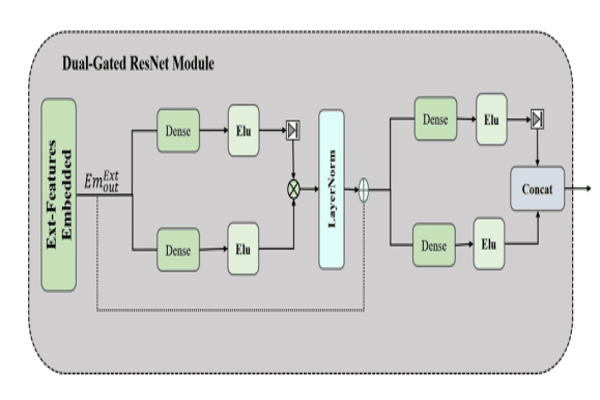 STTG-TTE: Spatial–Temporal Gated Multi-Modality Approach for Travel Time Estimation Based on Temporal Convolutional NetworksAlfateh M. Tag Elsir, Khaled Alkilane, and Yanming ShenNeural Computing and Applications, 2023
STTG-TTE: Spatial–Temporal Gated Multi-Modality Approach for Travel Time Estimation Based on Temporal Convolutional NetworksAlfateh M. Tag Elsir, Khaled Alkilane, and Yanming ShenNeural Computing and Applications, 2023Travel time forecasting has become a core component of smart transportation systems, which assists both travelers and traffic organizers with route planning, travel schedule adjustments, ride-sharing, navigation applications, and efficient traffic management. However, timely and accurate travel time forecasting still remains a critical challenge owing to the complex nonlinear and dynamic fluctuations of spatial–temporal dependencies. Also, spatial sparseness is a big issue in traffic forecasting, since adopting the implicit interactions between the close traffic regions leads to superficial characterization of spatio-temporal dependences. In this paper, we propose a new deep learning-based framework (STTG-TTE) that addresses these drawbacks and improves the travel time estimation. First, we build a geo-hashing algorithm for the data sparsity issue that incorporates fluctuations of nearby and distant traffic situations in terms of spatio-temporal dependencies. Second, a new spatio-temporal correlation modeling method is proposed to fully leverage large-scale spatial and temporal traffic patterns using temporal convolutional networks integrated with a gated multi-modality mechanism. Then, for external factors’ representation, a new dual-gated Res-Net multi-modality-based module is proposed. Finally, we fuse these representations of multi-components dynamically and utilize the transformer model, which is conducive to learning intersections among these multiple factors for obtaining accurate prediction results. Experiments on two largescale real-world traffic datasets from two different urban regions (Chengdu taxi-datsets and NYC-Bike datasets) demonstrate that the proposed model is superior to state-of-the-art baseline models.
@article{tag_elsir2023sttg, author = {Elsir, Alfateh M. Tag and Alkilane, Khaled and Shen, Yanming}, title = {STTG-TTE: Spatial–Temporal Gated Multi-Modality Approach for Travel Time Estimation Based on Temporal Convolutional Networks}, journal = {Neural Computing and Applications}, year = {2023}, volume = {35}, number = {7}, pages = {5535-5551}, doi = {10.1007/s00521-022-07977-w}, url = {https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-022-07977-w}, } - Neural Comput. Appl.
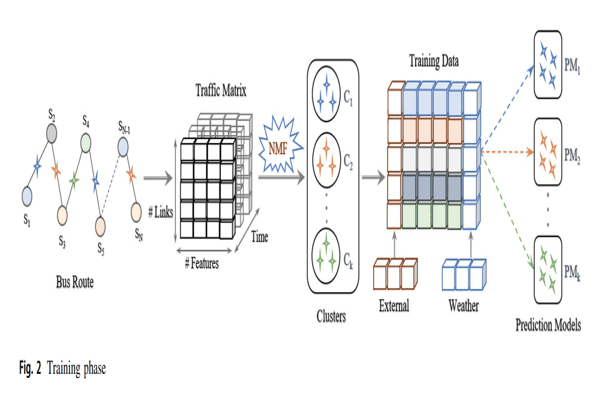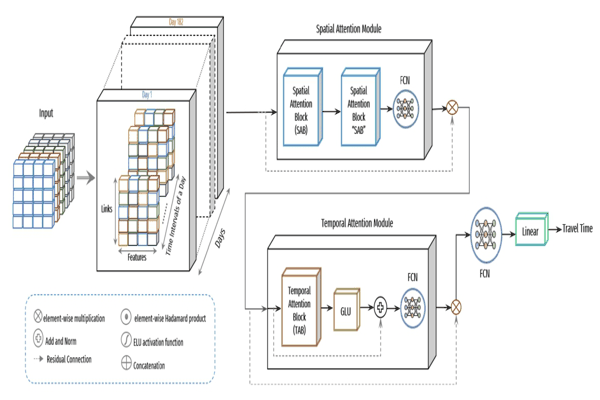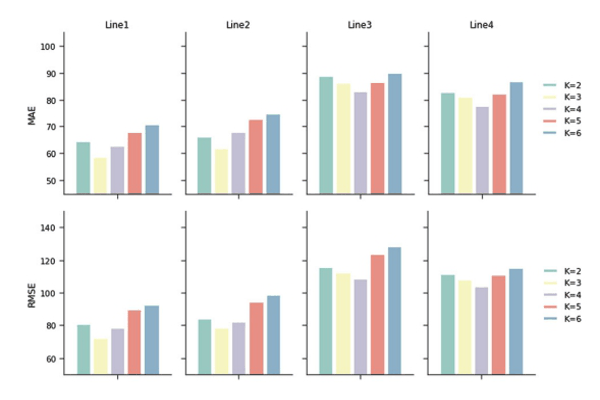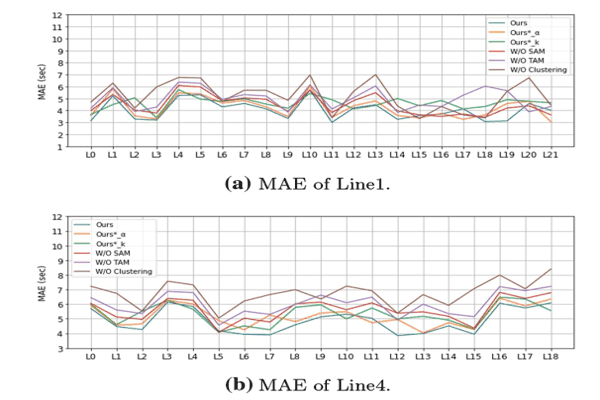 Travel Time Prediction Based on Route Links’ SimilarityKhaled Alkilane, M. Tag Elsir Alfateh, and Yanming ShenNeural Computing and Applications, 2023
Travel Time Prediction Based on Route Links’ SimilarityKhaled Alkilane, M. Tag Elsir Alfateh, and Yanming ShenNeural Computing and Applications, 2023Accurate travel time prediction allows passengers to schedule their journeys efficiently. However, cyclical factors (time intervals of the day, weather conditions, and holidays), unpredictable factors (incidents, abnormal weather), and other complicated factors (dynamic traffic conditions, dwell times, and variation in travel demand) make accurate bus travel time prediction complicated. This paper aims to achieve accurate travel time prediction. To do so, we propose a clustering method that identifies travel time paradigms of different route links and clusters them based on their similarity using the nonnegative matrix factorization algorithm. Additionally, we propose a deep learning model based on CNN with spatial–temporal attention and gating mechanisms to select the most relevant features and capture their dependencies and correlations. For each defined cluster, we train a separate model to predict the travel time at various time intervals over the day. As a result, the travel times of all journey links from related prediction models are aggregated to predict the total journey time. Extensive experiments using data collected from four different bus lines in Beijing show that our method outperforms the compared baselines.
@article{alkilane2023travel, author = {Alkilane, Khaled and Alfateh, M. Tag Elsir and Shen, Yanming}, title = {Travel Time Prediction Based on Route Links’ Similarity}, journal = {Neural Computing and Applications}, year = {2023}, volume = {35}, number = {5}, pages = {3991-4007}, doi = {10.1007/s00521-022-07926-7}, url = {https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-022-07926-7}, }
2022
- KBS
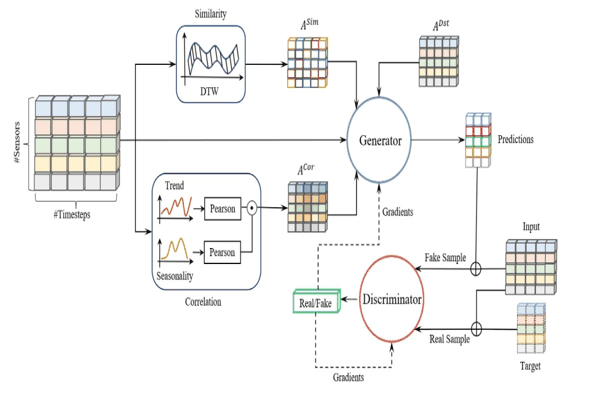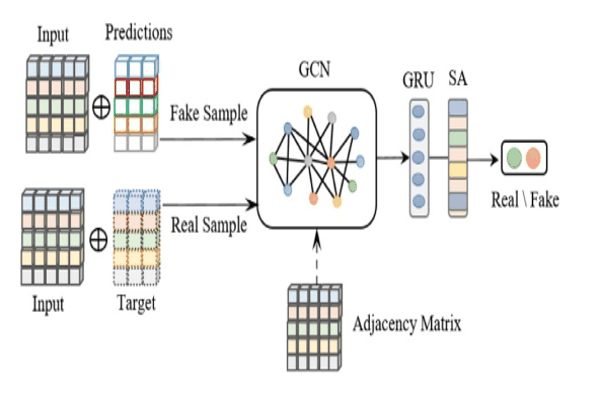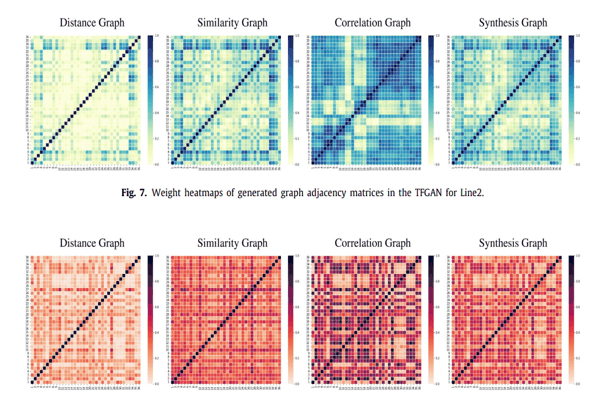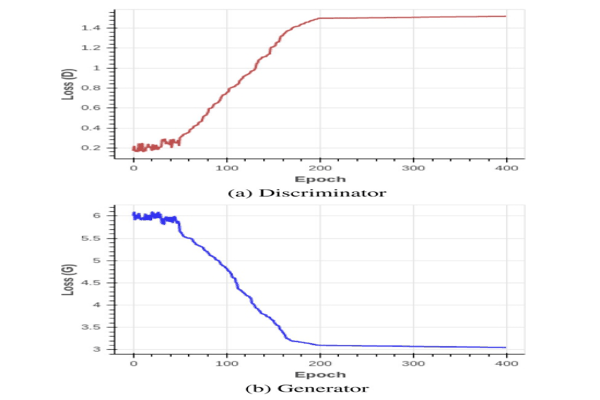 TFGAN: Traffic forecasting using generative adversarial network with multi-graph convolutional networkKhaled Alkilane, Alfateh M. Tag Elsir, and Yanming ShenKnowledge-Based Systems, 2022
TFGAN: Traffic forecasting using generative adversarial network with multi-graph convolutional networkKhaled Alkilane, Alfateh M. Tag Elsir, and Yanming ShenKnowledge-Based Systems, 2022Traffic forecasting constitutes a task of great importance in intelligent transport systems. Owing to the non-Euclidean structure of traffic data, the complicated spatial correlations, and the dynamic temporal dependencies, it is challenging to predict traffic accurately. Despite the fact that few prior studies have considered the interconnections between multiple traffic nodes at the same timestep, the majority of studies fail to capture the dependencies among multiple nodes at different timesteps. Furthermore, most existing work generates shallow graphs based solely on the distance between traffic nodes, which limits their representation competence and declines their power in capturing complex correlations. In particular, inspired by the recent breakthroughs in the generative adversarial network (GAN) and the power of the graph convolution network (GCN) in handling non-Euclidean data, this paper puts forward an adversarial multi-graph convolutional neural network model, named TFGAN, to address the abovementioned problems. We integrate the unsupervised model elasticity with the supervision provided by supervised training to help the GAN generator model generates accurate traffic predictions. To improve the representation and model the implicit correlations effectively, multiple GCNs are constructed within the generator based on various perspectives, such as similarity, correlation, and spatial distance. Meanwhile, GRU and self-attention are applied after each graph to capture the dynamic temporal dependencies across nodes. The comprehensive experiments on three different traffic variables (traffic flow, speed, and travel time) using six real-world traffic datasets demonstrate that TFGAN outperforms the related state-of-the-art models and achieves significant results.
@article{KHALED2022108990, title = {TFGAN: Traffic forecasting using generative adversarial network with multi-graph convolutional network}, journal = {Knowledge-Based Systems}, volume = {249}, pages = {108990}, year = {2022}, issn = {0950-7051}, doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2022.108990}, url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0950705122004804}, author = {Alkilane, Khaled and Elsir, Alfateh M. Tag and Shen, Yanming}, keywords = {Traffic forecasting, Multivariate time series, Generative adversarial network, Graph convolution network}, } - J. Adv. Transp.
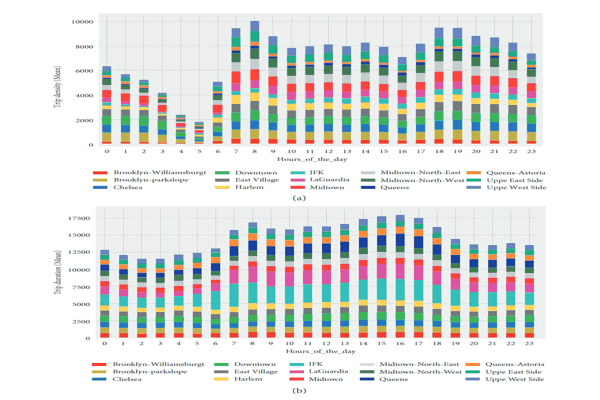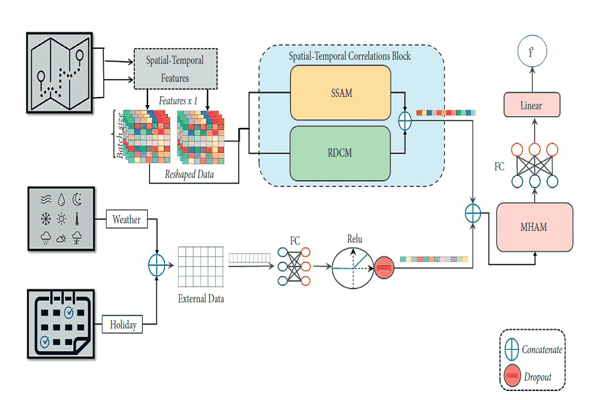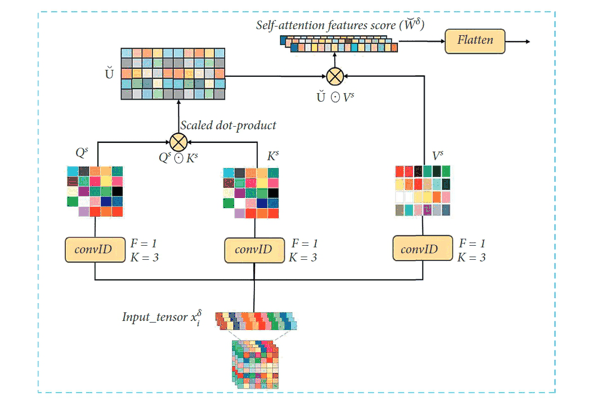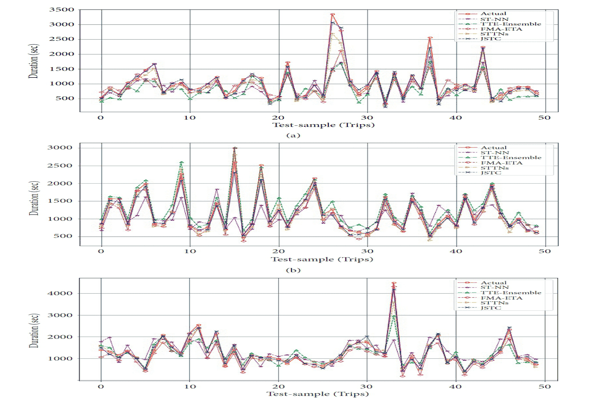 JSTC: Travel Time Prediction with a Joint Spatial-Temporal Correlation MechanismTag Elsir Alfateh M., Khaled Alkilane, Pengfei Wang, and 1 more authorJournal of Advanced Transportation, 2022
JSTC: Travel Time Prediction with a Joint Spatial-Temporal Correlation MechanismTag Elsir Alfateh M., Khaled Alkilane, Pengfei Wang, and 1 more authorJournal of Advanced Transportation, 2022Accurate travel time prediction is one of the most promising intelligent transportation system (ITS) services, which can greatly support route planning, ride-sharing, navigation applications, and effective traffic management. Several factors, like spatial, temporal, and external, have big effects on traffic patterns, and therefore, it is important to develop a mechanism that can jointly capture correlations of these components. However, spatial sparsity issues make travel time prediction very challenging, especially when dealing with the origin-destination (OD) method, since the trajectory data may not be available. In this paper, we introduce a unified deep learning-based framework named joint spatial-temporal correlation (JSTC) mechanism to improve the accuracy of OD travel time prediction. First, we design a spatiotemporal correlation block that combines two modules: self-convolutional attention integrated with a temporal convolutional network (TCN) to capture the spatial correlations along with the temporal dependencies. Then, we enhance our model performance through adopting a multi-head attention module to learn the attentional weights of the spatial, temporal, and external features based on their contributions to the output and speed up the training process. Extensive experiments on three large-scale real-world traffic datasets (NYC, Chengdu, and Xi’an) show the efficiency of our model and its superiority compared to other methods.
@article{https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/1213221, author = {M., Tag Elsir Alfateh and Alkilane, Khaled and Wang, Pengfei and Yanming, Shen}, title = {JSTC: Travel Time Prediction with a Joint Spatial-Temporal Correlation Mechanism}, journal = {Journal of Advanced Transportation}, volume = {2022}, number = {1}, pages = {1213221}, doi = {https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/1213221}, url = {https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1155/2022/1213221}, eprint = {https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1155/2022/1213221}, year = {2022} } - Neural Comput. Appl.
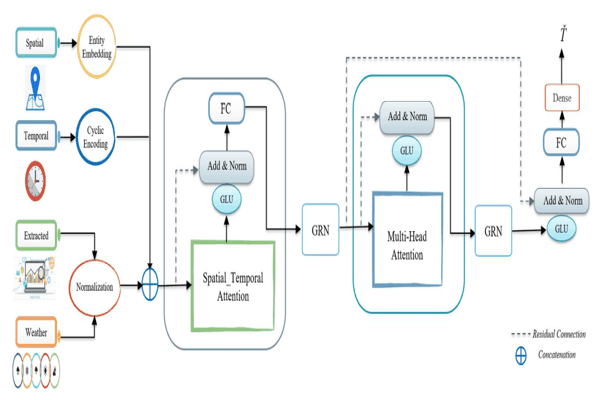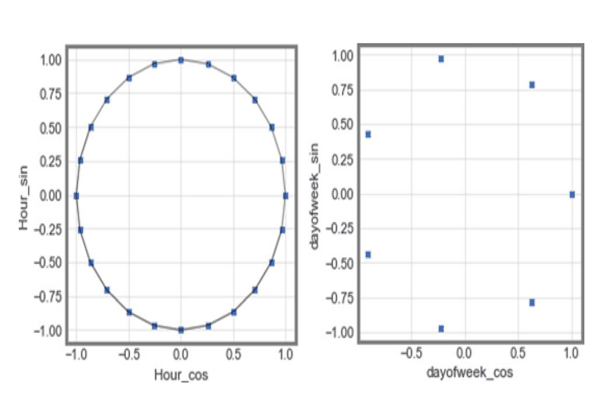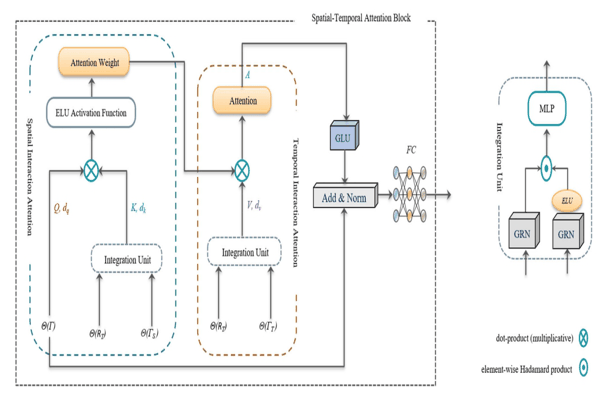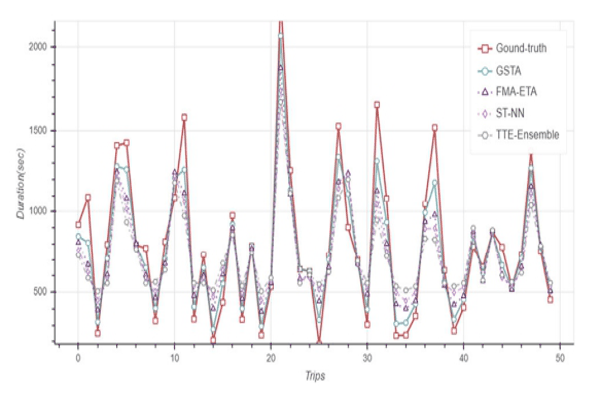 GSTA: Gated Spatial–Temporal Attention Approach for Travel Time PredictionKhaled Alkilane, Alfateh M. Tag Elsir, and Yanming ShenNeural Computing and Applications, 2022
GSTA: Gated Spatial–Temporal Attention Approach for Travel Time PredictionKhaled Alkilane, Alfateh M. Tag Elsir, and Yanming ShenNeural Computing and Applications, 2022Accurate travel time prediction between two locations is one of the most substantial services in transport. In travel time prediction, origin–destination (OD) method is more challenging since it has no intermediate trajectory points. This paper puts forward a deep learning-based model, called Gated Spatial–Temporal Attention (GSTA), to optimize the OD travel time prediction. While many trip features are available, their relations and particular contributions to the output are usually unknown. To give our model the flexibility to select the most relevant features, we develop a feature selection module with an integration unit and a gating mechanism to pass or suppress the trip feature based on its contribution. To capture spatial–temporal dependencies and correlations in the short and long term, we propose a new pair-wise attention mechanism with spatial inference and temporal reasoning. In addition, we adapt and integrate multi-head attention to improve model performance in case of sophisticated dependencies in long term. Extensive experiments on two large taxi datasets in New York City, USA, and Chengdu, China demonstrate the superiority of our model in comparison with other models.
@article{khaled2022gsta, author = {Alkilane, Khaled and Elsir, Alfateh M. Tag and Shen, Yanming}, title = {GSTA: Gated Spatial–Temporal Attention Approach for Travel Time Prediction}, journal = {Neural Computing and Applications}, year = {2022}, volume = {34}, number = {3}, pages = {2307-2322}, doi = {10.1007/s00521-021-06560-z}, url = {https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-021-06560-z}, }





